Carbon Capture
The EU promotes research and innovation for systems for capturing and storing CO2 from the atmosphere, which is responsible for the greenhouse effect and therefore for the rise in temperatures.
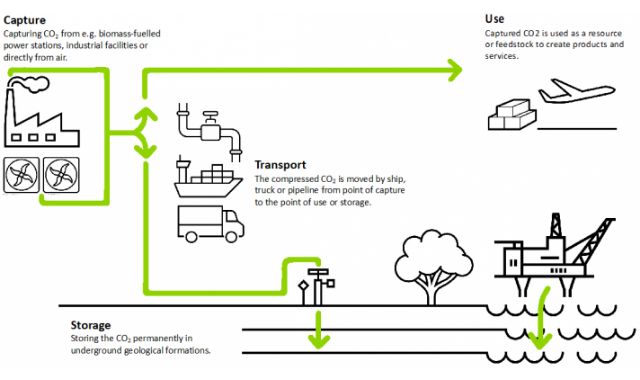
Although the least expensive system is to preserve the natural environment, given that CO2 is the bread for the plant kingdom, systems for carbon capture and storage (CCS) have been sought for years, a set of technologies aimed at capturing , transport and store the CO2 emitted by power plants and industrial plants.
The goal of CCS is to prevent CO2 from reaching the atmosphere by storing it in suitable underground geological formations. As a significant amount of power generation and industry will continue to rely on fossil fuels well into the future, the use of CCS is important to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon capture projects
|
Despite EU regulations and co-financing opportunities provided through the European Energy Recovery Program and NER300, carbon capture and storage have failed to develop at the expected pace, until now.
In 2013, the European Commission reviewed the progress of CCS and found that more than 20 small-scale CCS demonstration projects are operational globally but none in Europe and that at current low carbon prices, companies do not have a economic interest in investing in CCS. Furthermore a first generation CCS power plant is 60% to 100% more expensive than a conventional power plant. However, the Commission expects the cost of CCS to decrease over the long term as a result of R&D and the creation of economies of scale. Nevertheless, the EU is financing research for capturing carbon dioxide and to assess the future of various techniques. |
EU legislation on Carbon stockage
|
The European Union has been progressively implementing legislation and policies to regulate and encourage carbon storage as part of its broader strategy to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Here's an overview of the key aspects of EU legislation related to carbon storage:
|
- Innovation Fund: The Innovation Fund is one of the world's largest funding programs for the demonstration of innovative low-carbon technologies. Financed by the EU ETS, the fund aims to support innovative low-carbon technologies, including those for carbon capture, use, and storage.
- Green Deal and European Climate Law: The European Green Deal and the European Climate Law set out ambitious targets for the EU to become climate-neutral by 2050. These legislative frameworks emphasize the need for carbon removal technologies and practices, including reforestation, afforestation, carbon farming, and technological solutions like CCS.
- Circular Economy Action Plan: The Circular Economy Action Plan, updated in 2020, includes proposals to develop an effective and robust certification framework for carbon removals. This framework is intended to ensure the quality of carbon removals and to incentivize their uptake in the EU.
- Sustainable Carbon Cycles Communication: This communication sets the vision for enabling sustainable carbon cycles and emphasizes the role of carbon farming and the development of an internal market for CO2 capture, use, storage, and transport.
- Proposal for Amending the LULUCF Regulation: The European Commission has proposed amendments to the LULUCF Regulation to introduce a separate land-based net removals target, thus increasing the ambition for carbon removals through land use policies. European Parliament Opinion here.
EU legislation on carbon storage encompasses a range of directives, regulations, and action plans that address various aspects of carbon capture, use, and storage, as well as land use practices that contribute to carbon sequestration. These legislative measures are integral to the EU's broader strategy for achieving its climate goals and transitioning to a low-carbon economy.