The European Union Emissions Trading System - EU ETS is the European trading system for greenhouse gas emissions quotas. It is the main tool adopted by the European Union to achieve CO2 reduction objectives in the main industrial sectors and in the aviation sector. Introduced by Directive 2003/87/EC, the mechanism establishes an overall maximum ceiling on emissions allowed on the European territory in the sectors concerned, which corresponds to an equivalent number of allowances that can be bought/sold on a specific exchange market.
Each industrial operator active in the sectors covered by the scheme must "offset" its actual emissions (verified by an independent third party) on an annual basis with a corresponding amount of allowances. The accounting of the compensations is kept through the Single Union Register while the control over deadlines and compliance with the rules of the mechanism is entrusted to the National Competent Authorities.
The shares can be allocated against payment or free of charge. In the first case, they are sold through public auctions in which accredited subjects participate who buy mainly to offset their emissions. And they can also be traded on the secondary carbon market. In the second case, the quotas are assigned free of charge to operators at risk of relocation of production to countries characterized by less stringent environmental standards than European ones.
Each industrial operator active in the sectors covered by the scheme must "offset" its actual emissions (verified by an independent third party) on an annual basis with a corresponding amount of allowances. The accounting of the compensations is kept through the Single Union Register while the control over deadlines and compliance with the rules of the mechanism is entrusted to the National Competent Authorities.
The shares can be allocated against payment or free of charge. In the first case, they are sold through public auctions in which accredited subjects participate who buy mainly to offset their emissions. And they can also be traded on the secondary carbon market. In the second case, the quotas are assigned free of charge to operators at risk of relocation of production to countries characterized by less stringent environmental standards than European ones.
Auctioning
|
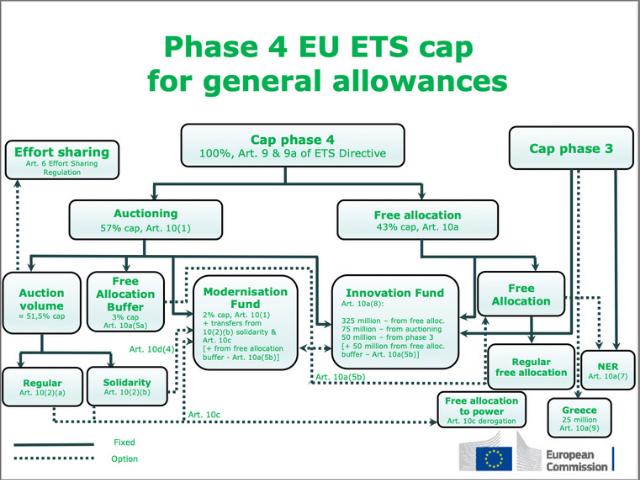
Auctioning is the most transparent method for allocating emission allowances and puts into practice the principle that the polluter should pay. Businesses covered by the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) have to buy an increasing proportion of allowances through auctions. On 14 July 2021, the European Commission adopted a series of legislative proposals setting out how it intends to achieve climate neutrality in the EU by 2050, including the intermediate target of an at least 55% net reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030. The package proposes to revise several pieces of EU climate legislation, including the EU ETS, Effort Sharing Regulation, transport and land use legislation, setting out in real terms the ways in which the Commission intends to reach EU climate targets under the European Green Deal.
From 2021, the UK is no longer part of the EU, however, pursuant to the Protocol of Ireland and Northern Ireland, the EU ETS applies to electricity generation located in Northern Ireland. Therefore, the UK will auction a small volume of allowances corresponding to its share in the Union-wide cap. The allowances made available to the Innovation Fund and to the Modernisation Fund are auctioned too. Allowances for the stationary installations (general allowances) are auctioned, unless they are allocated for free or placed in the Market Stability Reserve (MSR). In total, the Commission estimated that 57% of the total amount of general allowances were auctioned in phase 3. In phase 4 (2021-2030), the share of allowances to be auctioned remains the same. In accordance with the ETS Directive, in the aviation sector, 15% of all issued aviation allowances are auctioned (see FAQ). The Member States’ auction shares of general allowances and aviation allowances for phase 4 are published in Commission Decision (EU) 2020/2166 of 17 December 2020. |
|
Auction platforms
28 countries (25 EU Member States and 3 EEA/EFTA countries) auction their allowances on the common auction platform. To this end, they have signed a Joint Procurement Agreement.
Currently, the European Energy Exchange (EEX) in Leipzig is the common auction platform.
Germany and Poland have opted-out of the common auctioning platform. Germany has nominated EEX as its opt-out platform, while Poland is making use of the common auction platform (EEX) to auction its allowances until further notice.
The common auction platform is nominated for up to five years by a joint procurement between the Commission and the participating countries, in accordance to the rules laid down by the Joint Procurement Agreement.
For third parties, the Commission is the sole point of contact for information concerning the joint procurement procedures.
The procurement procedures are published on Tender Electronic Daily (e-Ted). Documents on past and ongoing tenders are also accessible via the contracts and grants pages.
28 countries (25 EU Member States and 3 EEA/EFTA countries) auction their allowances on the common auction platform. To this end, they have signed a Joint Procurement Agreement.
Currently, the European Energy Exchange (EEX) in Leipzig is the common auction platform.
Germany and Poland have opted-out of the common auctioning platform. Germany has nominated EEX as its opt-out platform, while Poland is making use of the common auction platform (EEX) to auction its allowances until further notice.
The common auction platform is nominated for up to five years by a joint procurement between the Commission and the participating countries, in accordance to the rules laid down by the Joint Procurement Agreement.
For third parties, the Commission is the sole point of contact for information concerning the joint procurement procedures.
The procurement procedures are published on Tender Electronic Daily (e-Ted). Documents on past and ongoing tenders are also accessible via the contracts and grants pages.
Auctioning revenues and their use
The total revenues generated by Member States, the UK and EEA countries from the auctions between 2012 and 30 June 2020 exceeded EUR 57 billion.
In 2019 alone, the generated total revenues were above EUR 14 billion, while in the first half of 2020 they reached EUR 7.9 billion.
The ETS Directive provides that Member States should use at least 50% of auctioning revenues or the equivalent in financial value for climate and energy-related purposes. Based on the most recent information, around 78% of revenues in 2013-2019 were used for climate and energy related purposes.
Member States are requested to report annually on the amounts and use of the revenues generated, under the Regulation on the Governance of the Energy Union and Climate Action. The total figures are annually reported in the Carbon Market Report.
Source: European Union, http://www.europa.eu/, 1998-2024
|
Brussels - Milano - Nice - Tokyo
|
eEuropa Belgium
Avenue Louise, 367 1050 Brussels BELGIUM Bld. Franck Pilatte, 19 bis
06300 Nice FRANCE YONO HOUSE 9-1 KAMIOCHIAI, SAITAMA-SHI, SAITAMA-KEN 〒 338-0001 JAPAN Via S. Veniero 6 20148 Milano ITALY |
All rights reserved - © Copyright eEuropa Belgium 2020-2024