|
Last updates: |
|
Vaccination
Vaccination is the primary tool for primary disease prevention and one of the most affordable public health measures available.
Immunization through vaccination is the best defense we have against serious, preventable and sometimes fatal contagious diseases.
Thanks to widespread vaccination, smallpox has been eradicated, Europe has made polio-free Europe and many other diseases have almost been eliminated.
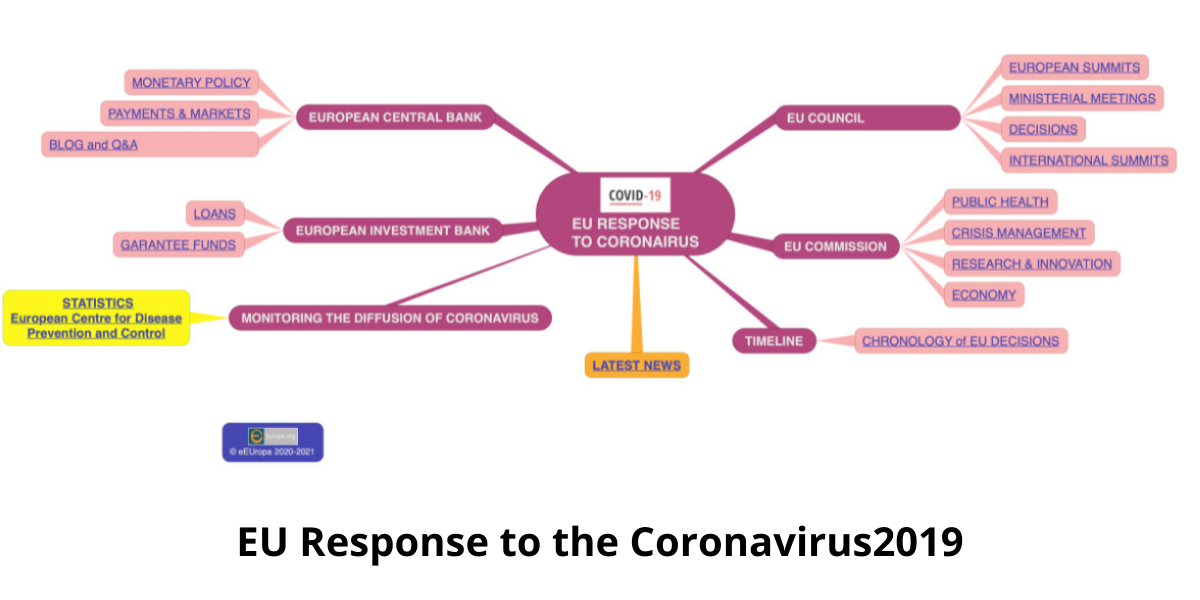
The EU Strategy against New Coronavirus
|
Challenges: vaccine acceptance
Despite the health success of vaccination campaigns around the world, the same success is not found among the population.
For example, more than 100 million children around the world are vaccinated every year against diseases such as diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, tuberculosis, polio, measles and hepatitis B. And these vaccination campaigns save the lives of approximately 2-3 million. children. every year.
Despite the success of vaccines already widely used to mitigate the aggressiveness of SARS-CoV 2, the vaccination rate in Western countries remains insufficient, due to the distrust of citizens.
This problem, coupled with geographic differences in accessibility and growing misinformation about vaccination, is a cause for concern and a major challenge for public health experts.
The public does not always know that there are very strict rules within the EU for the approval of any vaccine placed on the market. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) carries out the evaluation and supervision of vaccines once they are designed. Following very thorough testing, the European Commission can then issue a marketing authorization. After the approval of the National Medicines Agencies and once they are placed on the market, the EMA and the National Agencies continue to evaluate the safety of vaccines and carry out post-authorization surveillance.
Vaccines contain antigens that confer immunity against specific pathogens, such as the flu virus. However, for vaccines to be effective, they must also contain a number of other substances, including stabilizers, adjuvants and preservatives.
Stabilizers are needed to maintain the efficacy of the vaccine during storage. Adjuvants, on the other hand, are compounds added to vaccines to enhance the immune response. By stimulating the production of antibodies against a virus or bacterium, they make vaccines more efficient and long-lasting. Preservatives are a third type of compound essential to prevent the growth of dangerous bacteria or fungi, essential to ensure the safety of vaccines. All components of vaccines marketed in the European Union are subjected to careful scrutiny and, through various studies, have been found to be safe in the context of these vaccines. For information on vaccine safety, WHO offers a short online course on Vaccine Safety Basics.
In December 2021 the vaccination campaign continues, also with the administration of the third dose.
Action at EU level
Vaccination policy is a competence of national authorities, but the European Commission assists EU countries in coordinating their policies and programmes.
The Council adopted in December 2018 a Recommendation to strengthen the EU cooperation on vaccine-preventable diseases. The initiative aims to tackle vaccine hesitancy, improve coordination on vaccine procurement, support research and innovation, and strengthen EU cooperation on vaccine-preventable diseases.
EU countries are encouraged to develop and implement national vaccination plans with initiatives to improve coverage, and to introduce routine vaccination status checks.
Here the documentation:
In addition the Commission supports EU countries in maintaining or increasing rates of vaccination by:
The Council adopted in December 2018 a Recommendation to strengthen the EU cooperation on vaccine-preventable diseases. The initiative aims to tackle vaccine hesitancy, improve coordination on vaccine procurement, support research and innovation, and strengthen EU cooperation on vaccine-preventable diseases.
EU countries are encouraged to develop and implement national vaccination plans with initiatives to improve coverage, and to introduce routine vaccination status checks.
Here the documentation:
- Roadmap for the implementation of actions
- Council Recommendation
- Commission Communication
- Q&A
- Video (subtitles available in EN, FR, DE, IT, RO)
- Factsheet
- Consultation process
In addition the Commission supports EU countries in maintaining or increasing rates of vaccination by:
- Promoting seasonal flu vaccination to at risk groups.
- Encouraging EU countries to ensure that all children are immunised
- Authorising the use of three vaccines against cervical cancer
- Assisting EU countries in the development of a vaccination strategy against pandemic H1N1 influenza (or "swine flu")
Joint Action on vaccination
The European Commission is reinforcing its support to national vaccination efforts to increase coverage, including through the Joint Action on Vaccination co-funded by the EU Health Programme (EUR 3.55 million).
Launched in 2018, the Joint Action addresses vaccine hesitancy and seeks to increase vaccination coverage in the EU. It is coordinated by INSERM (France) and involves 20 partners (among them 17 EU countries and 3 non-EU countries).
It also works towards strengthening cooperation of national immunisation advisory groups (NITAGs) with a view to increasing transparency and trust in the decision-making process regarding the introduction of new vaccines.
Coalition for Vaccination
A Coalition for Vaccination was established in spring 2019. It brings together European associations of healthcare workers as well as relevant students´ associations in the field. The Coalition for Vaccination supports delivering accurate information to the public, fighting myths around vaccination and vaccines, and the exchange of best practices. It is currently co-chaired by three major European health professionals’ associations:
- the Standing Committee of European Doctors (CPME)
- the Pharmaceutical Group of the European Union (PGEU)
- the European Federation of Nurses Associations (EFN)
- To protect themselves from illness and possible severe or life-threatening complications
- COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective
- To help safeguard healthcare capacity
TIPS: If you want to be constantly informed on the ongoing legislative process in the European Institutions on EU Health Policy and take part to the debate, fill the form at the bottom of this page.